layout: post
categories: Linux
title: Teleport 跳板机部署[转载漠然]
date: 2017-11-09 16:47:51 +0800
description: Teleport 跳板机部署
keywords: Teleport 跳板机
由于业务需求,以前账号管理混乱,所以很多人有生产服务器的 root 权限;所以目前需要一个能 ssh 登录线上服务器的工具,同时具有简单的审计功能;找了好久找到了这个小工具,以下记录一下搭建教程
一、环境准备
目前准备了 3 台虚拟机,两台位于内网 NAT 之后,一台位于公网可以直接链接;使用时客户端通过工具连接到公网跳板机上,然后实现自动跳转到内网任意主机;并且具有相应的操作回放审计,通过宿主机账户限制用户权限
| ip | 节点 |
|---|---|
| 92.223.67.84 | 公网 Master |
| 172.16.0.80 | 内网 Master |
| 172.16.0.81 | 内网 Node |
二、Teleport 工作模式
Teleport 工作时从宏观上看是以集群为单位,也就是说公网算作一个集群,内网算作另一个集群,内网集群通过 ssh 隧道保持跟公网的链接状态,同时内网机群允许公网集群用户连接,大体工作模式如下
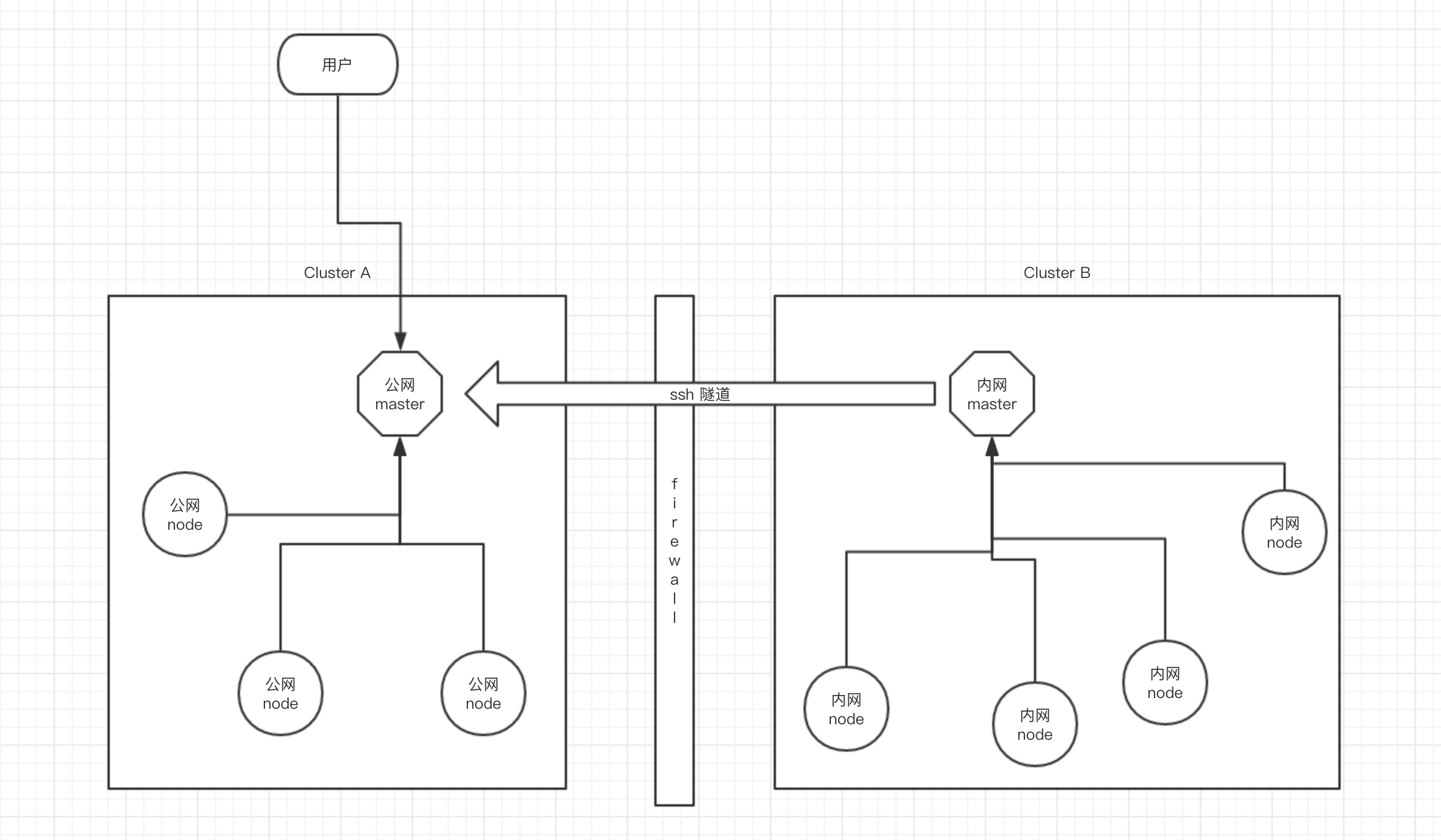
三、搭建公网 Master
3.1、配置 Systemd
首先下载相关可执行文件并复制到 Path 目录下,然后创建一下配置目录等
wget https://github.com/gravitational/teleport/releases/download/v2.3.5/teleport-v2.3.5-linux-amd64-bin.tar.gz
tar -zxvf teleport-v2.3.5-linux-amd64-bin.tar.gz
mv teleport/tctl teleport/teleport teleport/tsh /usr/local/bin
mkdir -p /etc/teleport /data/teleport
然后为了让服务后台运行创建一个 systemd service 配置文件
cat > /etc/systemd/system/teleport.service <<EOF
[Unit]
Description=Teleport SSH Service
After=network.target
[Service]
Type=simple
Restart=always
ExecStart=/usr/local/bin/teleport start -c /etc/teleport/teleport.yaml
[Install]
WantedBy=multi-user.target
EOF
3.2、配置 Teleport
Systemd 配置完成后,就需要写一个 Teleport 的配置文件来让 Teleport 启动,具体选项含义可以参考 官方文档;以下为我的配置样例
# By default, this file should be stored in /etc/teleport.yaml
# This section of the configuration file applies to all teleport
# services.
teleport:
# nodename allows to assign an alternative name this node can be reached by.
# by default it's equal to hostname
nodename: mritd.master
# Data directory where Teleport keeps its data, like keys/users for
# authentication (if using the default BoltDB back-end)
data_dir: /data/teleport
# one-time invitation token used to join a cluster. it is not used on
# subsequent starts
auth_token: jYektagNTmhjv9Dh
# when running in multi-homed or NATed environments Teleport nodes need
# to know which IP it will be reachable at by other nodes
advertise_ip: 92.223.67.84
# list of auth servers in a cluster. you will have more than one auth server
# if you configure teleport auth to run in HA configuration
auth_servers:
- 0.0.0.0:3025
- 0.0.0.0:3025
# Teleport throttles all connections to avoid abuse. These settings allow
# you to adjust the default limits
connection_limits:
max_connections: 1000
max_users: 250
# Logging configuration. Possible output values are 'stdout', 'stderr' and
# 'syslog'. Possible severity values are INFO, WARN and ERROR (default).
log:
output: stdout
severity: INFO
# Type of storage used for keys. You need to configure this to use etcd
# backend if you want to run Teleport in HA configuration.
storage:
type: bolt
# Cipher algorithms that the server supports. This section only needs to be
# set if you want to override the defaults.
ciphers:
- aes128-ctr
- aes192-ctr
- aes256-ctr
- aes128-gcm@openssh.com
- arcfour256
- arcfour128
# Key exchange algorithms that the server supports. This section only needs
# to be set if you want to override the defaults.
kex_algos:
- curve25519-sha256@libssh.org
- ecdh-sha2-nistp256
- ecdh-sha2-nistp384
- ecdh-sha2-nistp521
- diffie-hellman-group14-sha1
- diffie-hellman-group1-sha1
# Message authentication code (MAC) algorithms that the server supports.
# This section only needs to be set if you want to override the defaults.
mac_algos:
- hmac-sha2-256-etm@openssh.com
- hmac-sha2-256
- hmac-sha1
- hmac-sha1-96
# This section configures the 'auth service':
auth_service:
# Turns 'auth' role on. Default is 'yes'
enabled: yes
authentication:
# default authentication type. possible values are 'local', 'oidc' and 'saml'
# only local authentication (Teleport's own user DB) is supported in the open
# source version
type: local
# second_factor can be off, otp, or u2f
second_factor: otp
# this section is used if second_factor is set to 'u2f'
#u2f:
# # app_id must point to the URL of the Teleport Web UI (proxy) accessible
# # by the end users
# app_id: https://localhost:3080
# # facets must list all proxy servers if there are more than one deployed
# facets:
# - https://localhost:3080
# IP and the port to bind to. Other Teleport nodes will be connecting to
# this port (AKA "Auth API" or "Cluster API") to validate client
# certificates
listen_addr: 0.0.0.0:3025
# Pre-defined tokens for adding new nodes to a cluster. Each token specifies
# the role a new node will be allowed to assume. The more secure way to
# add nodes is to use `ttl node add --ttl` command to generate auto-expiring
# tokens.
#
# We recommend to use tools like `pwgen` to generate sufficiently random
# tokens of 32+ byte length.
tokens:
- "proxy,node:jYektagNTmhjv9Dh"
- "auth:jYektagNTmhjv9Dh"
# Optional "cluster name" is needed when configuring trust between multiple
# auth servers. A cluster name is used as part of a signature in certificates
# generated by this CA.
#
# By default an automatically generated GUID is used.
#
# IMPORTANT: if you change cluster_name, it will invalidate all generated
# certificates and keys (may need to wipe out /var/lib/teleport directory)
cluster_name: "mritd"
# This section configures the 'node service':
ssh_service:
# Turns 'ssh' role on. Default is 'yes'
enabled: yes
# IP and the port for SSH service to bind to.
listen_addr: 0.0.0.0:3022
# See explanation of labels in "Labeling Nodes" section below
labels:
role: master
# List of the commands to periodically execute. Their output will be used as node labels.
# See "Labeling Nodes" section below for more information.
commands:
- name: arch # this command will add a label like 'arch=x86_64' to a node
command: [uname, -p]
period: 1h0m0s
# enables reading ~/.tsh/environment before creating a session. by default
# set to false, can be set true here or as a command line flag.
permit_user_env: false
# This section configures the 'proxy servie'
proxy_service:
# Turns 'proxy' role on. Default is 'yes'
enabled: yes
# SSH forwarding/proxy address. Command line (CLI) clients always begin their
# SSH sessions by connecting to this port
listen_addr: 0.0.0.0:3023
# Reverse tunnel listening address. An auth server (CA) can establish an
# outbound (from behind the firewall) connection to this address.
# This will allow users of the outside CA to connect to behind-the-firewall
# nodes.
tunnel_listen_addr: 0.0.0.0:3024
# The HTTPS listen address to serve the Web UI and also to authenticate the
# command line (CLI) users via password+HOTP
web_listen_addr: 0.0.0.0:3080
# TLS certificate for the HTTPS connection. Configuring these properly is
# critical for Teleport security.
#https_key_file: /var/lib/teleport/webproxy_key.pem
#https_cert_file: /var/lib/teleport/webproxy_cert.pem
然后启动 Teleport 即可
systemctl enable teleport
systemctl start teleport
如果启动出现如下错误
error: Could not load host key: /etc/ssh/ssh_host_ecdsa_key
error: Could not load host key: /etc/ssh/ssh_host_ed25519_key
请执行 ssh-keygen 命令自行生成相关秘钥
ssh-keygen -t ecdsa -f /etc/ssh/ssh_host_ecdsa_key
ssh-keygen -t ed25519 -f /etc/ssh/ssh_host_ed25519_key
3.3、添加用户
公网这台 Teleport 将会作为主要的接入机器,所以在此节点内添加的用户将有权限登录所有集群,包括内网的另一个集群;所以为了方便以后操作先添加一个用户
# 添加一个用户名为 mritd 的用户,该用户在所有集群具有 root 用户权限
tctl --config /etc/teleport/teleport.yaml users add mritd root
添加成功后会返回一个 OTP 认证初始化地址,浏览器访问后可以使用 Google 扫描 OTP 二维码从而在登录时增加一层 OTP 认证
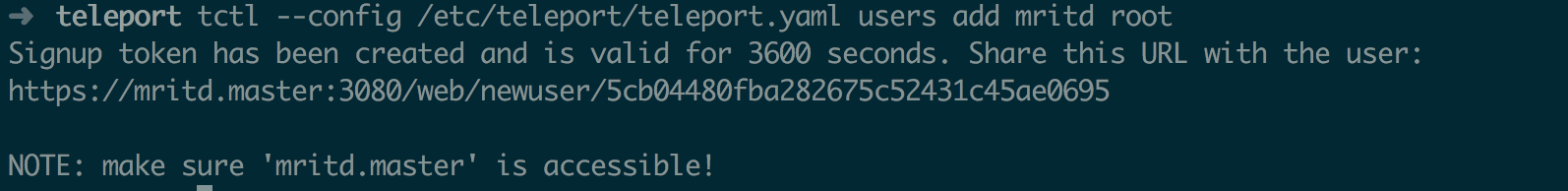
访问该地址后初始化密码及 OTP
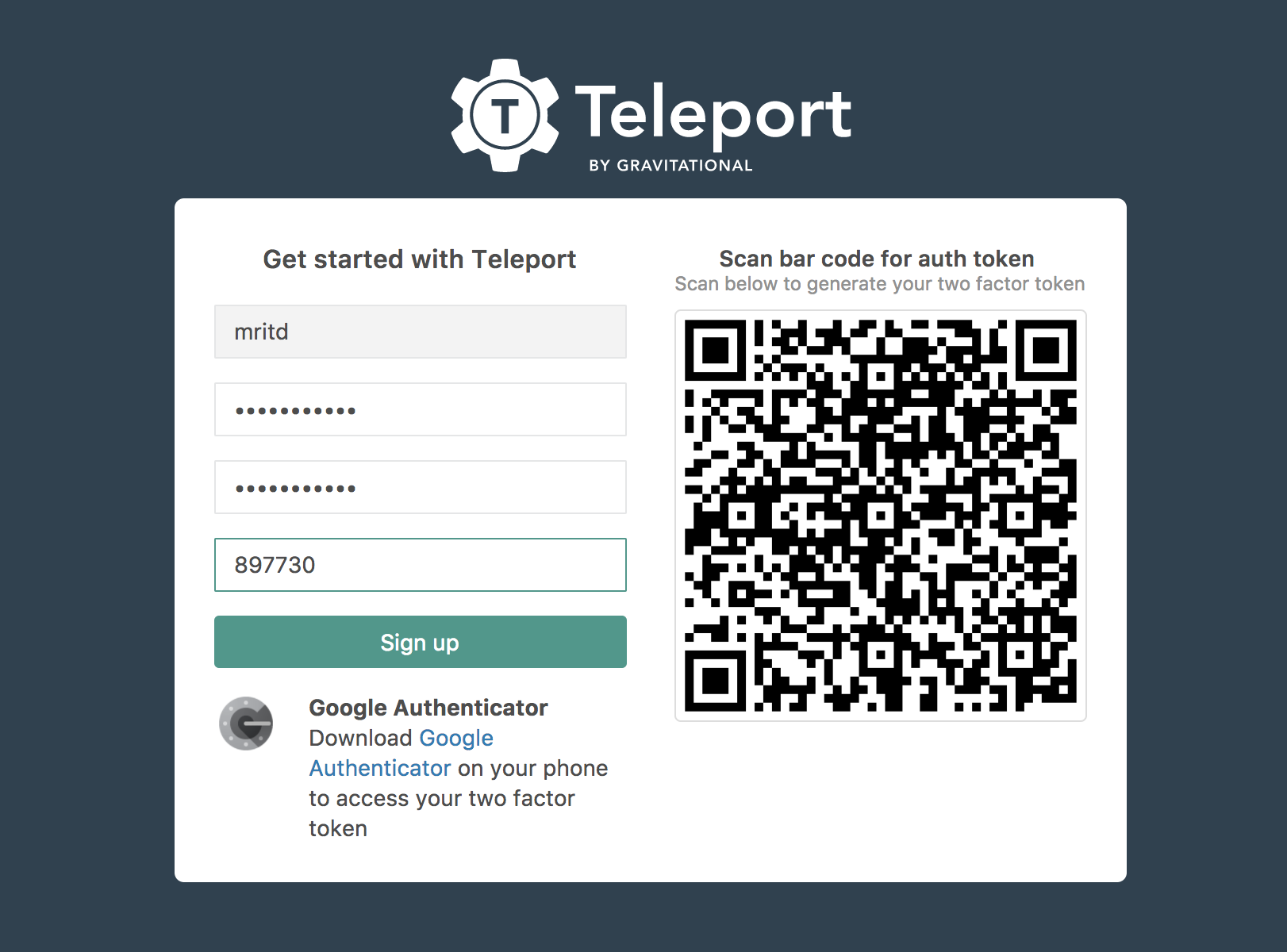
四、搭建内网 Master
内网搭建 Master 和公网类似,只不过为了安全将所有 0.0.0.0 的地址全部换成内网 IP 即可,以下为内网的配置信息
# By default, this file should be stored in /etc/teleport.yaml
# This section of the configuration file applies to all teleport
# services.
teleport:
# nodename allows to assign an alternative name this node can be reached by.
# by default it's equal to hostname
nodename: mritd.test1
# Data directory where Teleport keeps its data, like keys/users for
# authentication (if using the default BoltDB back-end)
data_dir: /data/teleport
# one-time invitation token used to join a cluster. it is not used on
# subsequent starts
auth_token: jYektagNTmhjv9Dh
# when running in multi-homed or NATed environments Teleport nodes need
# to know which IP it will be reachable at by other nodes
advertise_ip: 172.16.0.80
# list of auth servers in a cluster. you will have more than one auth server
# if you configure teleport auth to run in HA configuration
auth_servers:
- 172.16.0.80:3025
# Teleport throttles all connections to avoid abuse. These settings allow
# you to adjust the default limits
connection_limits:
max_connections: 1000
max_users: 250
# Logging configuration. Possible output values are 'stdout', 'stderr' and
# 'syslog'. Possible severity values are INFO, WARN and ERROR (default).
log:
output: stdout
severity: INFO
# Type of storage used for keys. You need to configure this to use etcd
# backend if you want to run Teleport in HA configuration.
storage:
type: bolt
# Cipher algorithms that the server supports. This section only needs to be
# set if you want to override the defaults.
ciphers:
- aes128-ctr
- aes192-ctr
- aes256-ctr
- aes128-gcm@openssh.com
- arcfour256
- arcfour128
# Key exchange algorithms that the server supports. This section only needs
# to be set if you want to override the defaults.
kex_algos:
- curve25519-sha256@libssh.org
- ecdh-sha2-nistp256
- ecdh-sha2-nistp384
- ecdh-sha2-nistp521
- diffie-hellman-group14-sha1
- diffie-hellman-group1-sha1
# Message authentication code (MAC) algorithms that the server supports.
# This section only needs to be set if you want to override the defaults.
mac_algos:
- hmac-sha2-256-etm@openssh.com
- hmac-sha2-256
- hmac-sha1
- hmac-sha1-96
# This section configures the 'auth service':
auth_service:
# Turns 'auth' role on. Default is 'yes'
enabled: yes
authentication:
# default authentication type. possible values are 'local', 'oidc' and 'saml'
# only local authentication (Teleport's own user DB) is supported in the open
# source version
type: local
# second_factor can be off, otp, or u2f
second_factor: otp
# this section is used if second_factor is set to 'u2f'
#u2f:
# # app_id must point to the URL of the Teleport Web UI (proxy) accessible
# # by the end users
# app_id: https://localhost:3080
# # facets must list all proxy servers if there are more than one deployed
# facets:
# - https://localhost:3080
# IP and the port to bind to. Other Teleport nodes will be connecting to
# this port (AKA "Auth API" or "Cluster API") to validate client
# certificates
listen_addr: 172.16.0.80:3025
# Pre-defined tokens for adding new nodes to a cluster. Each token specifies
# the role a new node will be allowed to assume. The more secure way to
# add nodes is to use `ttl node add --ttl` command to generate auto-expiring
# tokens.
#
# We recommend to use tools like `pwgen` to generate sufficiently random
# tokens of 32+ byte length.
tokens:
- "proxy,node:jYektagNTmhjv9Dh"
- "auth:jYektagNTmhjv9Dh"
# Optional "cluster name" is needed when configuring trust between multiple
# auth servers. A cluster name is used as part of a signature in certificates
# generated by this CA.
#
# By default an automatically generated GUID is used.
#
# IMPORTANT: if you change cluster_name, it will invalidate all generated
# certificates and keys (may need to wipe out /var/lib/teleport directory)
cluster_name: "nat"
# This section configures the 'node service':
ssh_service:
# Turns 'ssh' role on. Default is 'yes'
enabled: yes
# IP and the port for SSH service to bind to.
listen_addr: 172.16.0.80:3022
# See explanation of labels in "Labeling Nodes" section below
labels:
role: master
# List of the commands to periodically execute. Their output will be used as node labels.
# See "Labeling Nodes" section below for more information.
commands:
- name: arch # this command will add a label like 'arch=x86_64' to a node
command: [uname, -p]
period: 1h0m0s
# enables reading ~/.tsh/environment before creating a session. by default
# set to false, can be set true here or as a command line flag.
permit_user_env: false
# This section configures the 'proxy servie'
proxy_service:
# Turns 'proxy' role on. Default is 'yes'
enabled: yes
# SSH forwarding/proxy address. Command line (CLI) clients always begin their
# SSH sessions by connecting to this port
listen_addr: 172.16.0.80:3023
# Reverse tunnel listening address. An auth server (CA) can establish an
# outbound (from behind the firewall) connection to this address.
# This will allow users of the outside CA to connect to behind-the-firewall
# nodes.
tunnel_listen_addr: 172.16.0.80:3024
# The HTTPS listen address to serve the Web UI and also to authenticate the
# command line (CLI) users via password+HOTP
web_listen_addr: 172.16.0.80:3080
# TLS certificate for the HTTPS connection. Configuring these properly is
# critical for Teleport security.
#https_key_file: /var/lib/teleport/webproxy_key.pem
#https_cert_file: /var/lib/teleport/webproxy_cert.pem
配置完成后直接启动即可
systemctl enable teleport
systemctl start teleport
五、将内网集群链接至公网
上文已经讲过,Teleport 通过公网链接内网主机的方式是让内网集群向公网打通一条 ssh 隧道,然后再进行通讯;具体配置如下
5.1、公网 Master 开启授信集群
在公网 Master 增加 Token 配置,以允许持有该 Token 的其他内网集群连接到此,修改 /etc/teleport/teleport.yaml 增加一个 token 即可
tokens:
- "proxy,node:jYektagNTmhjv9Dh"
- "auth:jYektagNTmhjv9Dh"
- "trusted_cluster:xiomwWcrKinFw4Vs"
然后重启 Teleport
systemctl restart teleport
5.2、内网 Master 链接公网 Master
当公网集群开启了允许其他集群链接后,内网集群只需要创建配置进行连接即可,创建配置(cluster.yaml)如下
# cluster.yaml
kind: trusted_cluster
version: v2
metadata:
# the trusted cluster name MUST match the 'cluster_name' setting of the
# cluster
name: local_cluster
spec:
# this field allows to create tunnels that are disabled, but can be enabled later.
enabled: true
# the token expected by the "main" cluster:
token: xiomwWcrKinFw4Vs
# the address in 'host:port' form of the reverse tunnel listening port on the
# "master" proxy server:
tunnel_addr: 92.223.67.84:3024
# the address in 'host:port' form of the web listening port on the
# "master" proxy server:
web_proxy_addr: 92.223.67.84:3080
执行以下命令使内网集群通过 ssh 隧道连接到公网集群
tctl --config /etc/teleport/teleport.yaml create /etc/teleport/cluster.yaml
注意,如果在启动公网和内网集群时没有指定受信的证书( https_cert_file、https_key_file ),那么默认 Teleport 将会生成一个自签名证书,此时在 create 受信集群时将会产生如下错误:
the trusted cluster uses misconfigured HTTP/TLS certificate
此时需要在 待添加集群(内网) 启动时增加 --insecure 参数,即 Systemd 配置修改如下
[Unit]
Description=Teleport SSH Service
After=network.target
[Service]
Type=simple
Restart=always
ExecStart=/usr/local/bin/teleport start --insecure -c /etc/teleport/teleport.yaml
[Install]
WantedBy=multi-user.target
然后再进行 create 就不会报错
六、添加其他节点
两台节点打通后,此时如果有其他机器则可以将其加入到对应集群中,以下以另一台内网机器为例
由于在主节点 auth_service 中已经预先指定了一个 static Token 用于其他节点加入( proxy,node:jYektagNTmhjv9Dh ),所以其他节点只需要使用这个 Token 加入即可,在另一台内网主机上修改 Systemd 配置如下,然后启动即可
[Unit]
Description=Teleport SSH Service
After=network.target
[Service]
Type=simple
Restart=always
ExecStart=/usr/local/bin/teleport start --roles=node,proxy \
--token=jYektagNTmhjv9Dh \
--auth-server=172.16.0.80
[Install]
WantedBy=multi-user.target
此时在内网的 Master 上可以查看到 Node 已经加入
test1.node ➜ tctl --config /etc/teleport/teleport.yaml nodes ls
Hostname UUID Address Labels
----------- ------------------------------------ ---------------- -----------------------
test2.node abc786fe-9a60-4480-80f7-8edc20710e58 172.16.0.81:3022
mritd.test1 be9080fb-bdba-4823-9fb6-294e0b0dcce3 172.16.0.80:3022 arch=x86_64,role=master
七、连接测试
7.1、Web 测试
Teleport 支持 Web 页面访问,直接访问 https://公网IP:3080,然后登陆即可,登陆后如下
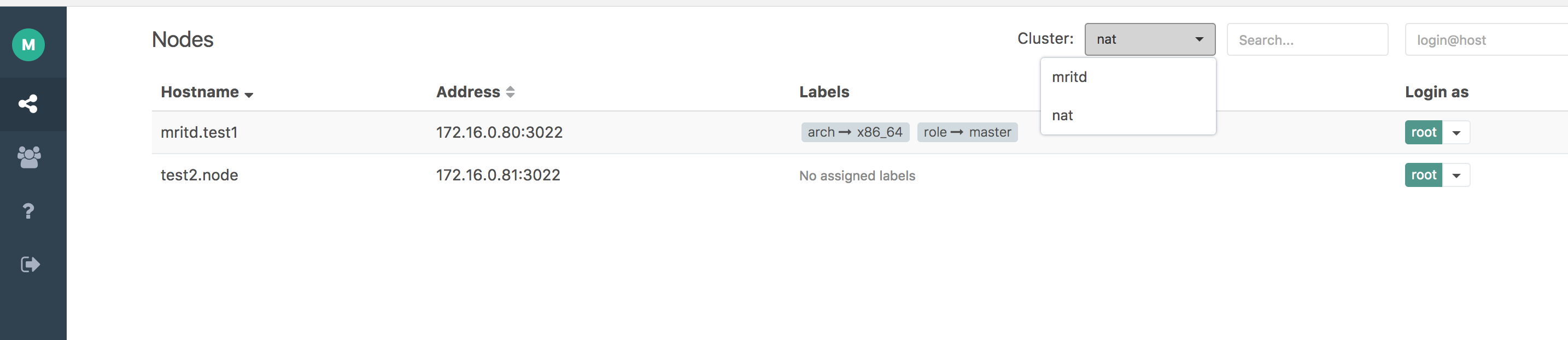
通过 Cluster 选项可以切换不同集群,点击后面的用户名可以选择不同用户登录到不同主机(用户授权在添加用户时控制),登陆成功后如下
通过 Teleport 进行的所有操作可以通过审计菜单进行操作回放

7.2、命令行测试
类 Uninx 系统下我们还是习惯使用终端登录,终端登录需要借助 Teleport 的命令行工具 tsh,tsh 在下载的 release 压缩版中已经有了,具体使用文档请自行 help 和参考官方文档,以下为简单的使用示例
- 登录跳板机: 短时间内只需要登录一次即可,登录时需要输入密码及 OTP 口令
export TELEPORT_PROXY=92.223.67.84
export TELEPORT_USER=mritd
tsh login --insecure
- 登录主机: 完成上一步 login 后就可以免密码登录任意主机
# cluster 名字是上面设置的,在 web 界面也能看到
tsh ssh --cluster nat root@test2.node
- 复制文件: 复制文件时不显示进度,并非卡死
tsh scp --cluster nat teleport-v2.3.5-linux-amd64-bin.tar.gz root@test2.node:/
-> teleport-v2.3.5-linux-amd64-bin.tar.gz (16797035)
转载请注明出处,本文采用 CC4.0 协议授权